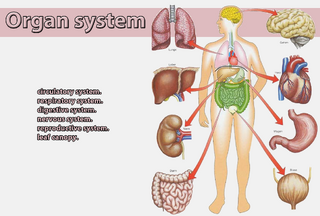
Organ system
Here are some examples of organ systems:
- circulatory system.
- respiratory system.
- digestive system.
- nervous system.
- reproductive system.
- leaf canopy.
The human body is made up of several organ systems that work together as one unit. Ten major organ systems of the body are listed below, along with several organs that are associated with each system.
Organ Systems
1. Circulatory System:[]
The main function of this system is to transport nutrients and gasses to cells and tissues throughout body. This is accomplished by the circulation of blood.
Cardiovascular: This system is comprised of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. The beating of the heart drives the cardiac cycle which pumps blood throughout body.
Cardiovascular organs: heart, blood vessels, blood
Lymphatic: This system is a vascular network of tubules and ducts that collect, filter, and return lymph to blood circulation. As a component of the immune system, the lymphatic system produces and circulates immune cells called lymphocytes.
Lymphatic organs: lymph vessels, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, tonsils
Biology
- Human Body Systems
- Immune System
- System Systems
- Disgestive System
2. Digestive System:[]
This system breaks down food polymers into smaller molecules to provide energy for the body. Digestive juices and enzymes are secreted to break down the carbohydrates, fat, and protein in food.
Primary organs: mouth, stomach, intestines, rectum
Accessory organs: teeth, tongue, liver, pancreas
3. Endocrine System:[]
This system regulates vital processes in the body including growth, homeostasis, metabolism, and sexual development. Endocrine organs secrete hormones to regulate body processes.
Endocrine structures: pituitary gland, pineal gland, thymus, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland
4. Integumentary System:[]
This system protects the internal structures of the body from damage, prevents dehydration, stores fat and produces vitamines and hormones.
Integumentary structures: skin, nails, hair, sweat glands
5. Muscular System:[]
This system enables movement through the contraction of muscles.
Structures: muscles
6. Nervous System:[]
This system monitors and coordinates internal organ function and responds to changes in the external environment.
Structures: brain, spinal cord, nerves
(See Neurosystem for more detail)
7. Reproductive System:[]
This system enables the production of offspring through sexual reproduction. It is comprised of male and female reproductive organs and structures which produce sex cells and ensure the growth and development of offspring.
Male organs: testes, scrotum, penis, vas deferens, prostate Female organs: ovaries, uterus, vagina, mammary glands
8. Respiratory System:[]
This system provides the body with oxygen via gas exchange between air from the outside environment and gases in the blood.
Respiratory organs: lungs, nose, trachea, bronchi
==9. Skeletal System:
==
It is important to keep in mind that these organ systems don't just exist as individual units. The final product of these cooperating systems is one unit called the body. Each system depends on the others, either directly or indirectly, to keep the body functioning normally.